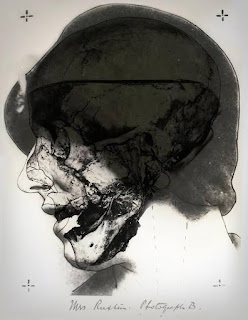
The Buck Ruxton "Jigsaw Murders" case Skull no. 2, photograph B, 1935 Investigators photographed the Skull No. 2 in the same orientation as an existing photograph of Mrs. Ruxton. Then they laid a photo-transparency of this skull over the portrait to establish that the skull was Mrs. Ruxton's. On September 14, 1935, Buck Ruxton, an Indian-born physician who lived in Lancashire, near the English-Scottish border, murdered his wife Isabella and her maid Mary Rogerson, and then mutilated their bodies and scattered the parts, in an effort to make them unidentifiable. After a passerby discovered some remains under a bridge in Scotland, a team of forensic experts was assembled. Using an array of scientific methods, the experts identified the victims and unmasked the perpetrator. The painstaking reconstruction of the bodies of Isabella Ruxton and Mary Rogerson by forensic pathologist John Glaister Jr. and anatomist James Couper Brash—and pioneering use of photographic superimpositions—was the key evidence that led to Dr. Ruxton's conviction and execution. The success of the methods used in the Ruxton case, which was widely reported in the press, led to increased public and professional trust in the capabilities of forensic science. Dr. Ruxton's trial, which took place in March 1936, lasted 11 days. He was found guilty and sentenced to be hanged to death. Before his execution, he admitted his guilt.
Dig into history, science, true crime, and beyond with All That's matters — where you'll discover the most interesting things that's matters
Search on Wikipedia
Search results
The first execution by electrocution in history, is carried out against William Kemmler

On August 6, 1890, at Auburn Prison in New York, the first execution by electrocution in history, is carried out against William Kemmler, who had been convicted of murdering his lover, Matilda Ziegler, with a hatchet. William had accused her of stealing from him, and preparing to run away with a friend of his... click image to read story
Search This Blog
holocaust.victims: Grietje van der Kar-Posno was born in Rotterdam on December 9, 1911. She was Jewish, the daughter of Heintje Snoek-Canes ...